Vertec Python functions
Description of the Vertec Python functions
Overview
- The global module “vtcapp”
- Features on individual objects:
- All Objects
- Projects
- Abstractworker (Project Editor user and Planning Editor)
- User
- Phases
- Invoices
- Project Entries (servicesservices expenses expensesoutlay
- Services
- Activities
- Currency
- Vertec Lists
- Other Python modules supplied by Vertec:
- Module “ziputils” for compressing files and creating .zip files
- Module “vtcextensions” for working with interfaces
- Modules “vtcplanning” and “vtcplanningcore” for working with resource planning
- Module “vtccom” for cloud-enabled cloud ready interface extensions via COM Forwarding
- Module “vtcauth” for logging in via OAuth
- Module “vtcmodel” for informations about the Vertec data model
The module “vtcapp”
The Vertec installation includes a Vertec Python library (module). This is available everywhere in Vertec, e.g. in Python scripts, and is called vtcapp. It has the following features:
| Function | Description | Sample code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
argobject |
Current Vertec object. This variable is always available, so the call can be made without |
project = argobject |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
bigetdata(source, dimensions, measures, from, till, currency=None) |
As of Vertec 6.8. Python feature for querying Business Intelligence (BI) data. For a detailed description, see the article Python feature for querying bi data |
projects = vtcapp.currentlogin().evalocl("ownprojects->select(active)") result = vtcapp.bigetdata(projects, ["Project"], ["FeesExt"], None, None) for project in projects: print("Fee: {}".format(result.get_value(project, "FeesExt"))) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
checkcreate(classname:string): int |
Checks whether the current session has user rights to create objects of the specified class. Returns 0 or 1 (False, True) |
>>> vtcapp.checkcreate('Project') 1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
checkfeature(featurecode: string): boolean |
Checks if a particular feature is licensed. The feature codes are according to Vertec feature matrix (e.g. Returns False or True |
>>> vtcapp.checkfeature('fcPhases') True |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
convertwordtopdf(wordDoc: string): string |
Converts a Word document of type |
(name, file) = vtcapp.requestfilefromclient("Select document", r"C:", "Word|*.docx") pdfDoc = vtcapp.convertwordtopdf(file) vtcapp.sendfile(pdfDoc, 'aFilename.pdf' , True) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
createoutlookmail(to, subject, body=”“, cc=”“, bcc=”“, attachments=[], show=True, onBehalfOf=”“)Python method from version 6.4.0.4, which creates to create an email message on the client via Outlook. Works with the Cloud App (and the Desktop App) and Outlook as a local Windows client. If you are working with the Web App or the New Outlook, the method sendmail() can be used (the “New OutlookOutlook for Windows is not a local Windows client, but a Web client, wrapped in a Windows program.
Optional:
*Keyword means that you can specify the optional values with the parameter as a keyword, e.g. Examples:
Note: Use tables in your Word documents and avoid tab stops, as they cannot be processed in the email.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
createlist(classname, [list]): list |
In this way, a Vertec list can be created, on which OCL can then be evaluated.
The python methods evalocl(), getwithsql(), and getmemberwithsql() automatically return vertec lists, see Vertec lists. |
mylist = vtcapp.createlist('Project') mylist.append(argobject) or by specifying list: mylist = vtcapp.createlist("Project", vtcapp.currentlogin().evalocl("ownprojects")) mylist2 = list.evalocl("self->select(active)") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
createobject(class: string) |
Creates new object of the specified class. |
leistung = vtcapp.createobject("OpenService") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
currentlogin(): User |
Current logged in user |
user = vtcapp.currentlogin()
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
currentobject |
Parent entry, see description in the article Register Register scripts. |
myobject = currentobject |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
disableevents() |
As of Vertec 6.7.0.7 always use Disabledevents() instead. With Used when you want to customize a certain attribute that would otherwise execute an event. Can be turned on again with Requires extended user rights. Not allowed in the Python Script editor for security reasons. |
try: vtcapp.disableevents() invoice.entrydate = vtcapp.currentdate() finally: vtcapp.enableevents() |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
DisabledEvents() |
As of version 6.7.0.7. Must include
Within this method, event scripting is turned off, affecting the entire Vertec session (other Vertec sessions or Desktop App are not affected). Used, for example, to modify a certain attribute that would otherwise execute an event. |
with vtcapp.DisabledEvents(): invoice.entrydate= vtcapp.currentdate() |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
evalocl(expression: string): expressiontype |
Evaluate global OCL expression. |
vtcapp.evalocl("user->select(active)") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
evaloclstring(obj: object, expStr: string): string |
Evaluate OCL expression within a string. Returns: fully evaluated string. |
>>> vtcapp.evaloclstring(argobject,"User %name% is %level.asstring%") User Christoph Keller is Senior Consultant |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
evaltovariable(obj: object, ocl: string, varname: string) |
Evaluates an OCL and saves the value in an OCL variable. The variable can then be queried globally with The variable name may be: |
vtcapp.evaltovariable(argobject, "invoices->first", "varInvoice") >>> vtcapp.evalocl("varInvoice") 25050018, IT Consulting |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
executefile(command: string, [argumentString: string])Feature to access files via Vertec Desktop App and Vertec Cloud App. Command Line Parameters are also supported. You can optionally pass arguments for this. The previous simple case still works. Parameter parsing is as follows:
Only files of the type
ExamplesTo open a Word file: path = r'S:\Documents\Contacts\Bistro Cooper\Letter.docx' vtcapp.executefile(path) The r in front of the path causes control characters to be ignored. Since the backslash is a control character in some combinations for Python, otherwise the path may be misinterpreted or fragmented, resulting in an error. Open a file in Notepad++, using command line parameters: vtcapp.executefile('notepad++.exe', r'-lpython "C:\Documents\My Script.py"') |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
executefolder(path: string) |
Opens the specified folder on the client (without Web App), e.g. in Windows Explorer. The path must be accessible from the client. If the folder does not exist yet, a message appears whether it should be created:  |
path = r'S:\Documents\Contacts\Bistro Cooper' vtcapp.executefolder(path) The r in front of the path causes control characters to be ignored. Since the backslash is a control character in some combinations for Python, otherwise the path may be misinterpreted and an error may occur. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
executereport(rootObj, optarg, reportObj, [saveAs, showDialog, doPrint, showApp]): reportAllows you to call and run Reports based on a report object. For
ExamplesShow a Word report for invoice without dialog and without saving a filesave rechTempl = vtcapp.evalocl("report->select(entryid='BerichtScriptInvoiceWithList')->first") vtcapp.executereport(argobject, None, rechTempl, "", showDialog=False) As of version 6.4.0.8 the method returns the report output as a byte string. This can be further processed and e.g. attached to an email via vtcapp.createoutlookmail(). invtempl = vtcapp.evalocl("report->select(entryid='BerichtScriptInvoiceWithList')->first") pdf = vtcapp.executereport(argobject, None, invtempl, "", showDialog=False) vtcapp.createoutlookmail("myemail@company.com", "aSubject", "aBody", attachments=[('invoice.pdf', pdf)]) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
executereport2(obj, optarg, template, [saveAs, showDialog, unused, showApp]): (report, activity) |
Starting with version 6.4.0.22. Allow calling and executing Reports based on a report object. The method returns a tuple consisting of the report output as a byte string and the corresponding activity. For the description of the parameters see executereport() above. For a table of availability with the different systems, see the section further down. |
template = vtcapp.evalocl("report->select(entryid='BerichtScriptInvoiceWithList')->first") reportdoc, activity = vtcapp.executereport2(argobject, None, template) The method returns a tuple:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
execututeurl(url) |
Opens the specified URL on the client (all full-featured apps). The URL must be accessible from the client. The Web App must be a publicly accessible path, access to the local client is not possible. |
For example, to open a website in the browser: vtcapp.executeurl("https://www.vertec.com") Or a Vertec Breadcrumb URL: vtcapp.executeurl("vertec://CK-676/Own+projects-49/COMINSTALL-2880/") the same also works as a short version, in which only the IDs are specified: vtcapp.executeurl("vertec://676/49/2880/") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
extractplaintext(file[, extension]): string |
Vertec 6.8 or later. Used to extract (unformatted) text from files. This method extracts the text from these input files (
Only content from cells formatted as
If the byte array does not represent any of these specified file types, or if extracting the content fails, an empty string is returned. By specifying an optional extension, the file type is not determined based on the transferred file, but is specified via extension. Thus, the following file types are valid: |
Document Storage Internal:
file = argobject.content
text = vtcapp.extractplaintext(file)
Document Storage File system/DMS: filename, file = vtcapp.requestfilefromclient("Select file", r"C:\Documents", "PDF|*.pdf|DOCX|*.docx|EML|*.eml|MIME|*.msg") text = vtcapp.extractplaintext(file) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
fetchlinkmembers(objectlist, membername): objectlist |
As of Vertec 6.4. Loads the sublist (membername) for a list of objects (objectlist) into memory, and at the same time makes the multilink current, which means that when the link is accessed, the list is not reloaded. Therefore, the call should fetchlinkmembers() immediately prior to the re-use of the list. |
# Loop through phases of projects that have at least one phase with the status "accepted". projekte = vtcapp.getwithsql("Project", "bold_id IN (SELECT project FROM phase WHERE status=1)", "") vtcapp.fetchlinkmembers(projekte, "phases") for projekt in projekte: x = projekt.evalocl("phases->select(status=1)") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
generateinvoicenumber() |
Generates the next Vertec invoice number according to system settings invoice / invoice. |
invoice = argobject
invoice.number = vtcapp.generateinvoicenumber()
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
getcurrentobject() |
Returns the selected object in the tree and can be called from Ocl call operators using OCL call operators. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
getmailattachment(content, idx): bytestring |
From version 6.5. Allow you to download an email attachment of an activity. Returns the contents of the attachment as a byte string. Since the names of the attachments are not necessarily unique, it must be identified by Idx. |
activity = argobject
filecontent = vtcapp.getmailattachment(activity.content, 0)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
getmailattachments(content): list(string) |
As of version 6.5. Return a list of attachment names of an activity. |
filenames = vtcapp.getmailattachments(activity.content)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
getmemberwithsql(obj: object, membername: string, where: string, order: string): list of objects |
Allows querying members of an object via SQL. The executing user must have administrator rights or the SQL Query right. The extended user rights variant is available for granting temporary administrator rights. |
project = argobject servicelist = vtcapp.getmemberwithsql(project, "openservices", "xfeeext>200", "") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
getobjectbyentryid(classname: string, entryid: string): object |
As of version 6.6.0.2. Get the object with the specified class and Entry Id Both parameters must always be specified. If the class If no or more objects are found, an error is thrown. Note: The objects are loaded internally via SQL. Thus, only objects already stored in the database are found. For newly created objects, a |
folder = vtcapp.getobjectbyentryid("Folder", "KeywordFolderAdministration") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
getobjectbyid(id: int, string or long*): object |
Gets the object with the specified Internal Id. If the id does not exist, an error is thrown. Note: The objects are loaded internally via SQL. Thus, only objects already stored in the database are found. For newly created objects, a * As of Vertec 6.7.0.4. |
obj = vtcapp.getobjectbyid(62162)
or obj = vtcapp.getobjectbyid("62162") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
getpropertyvalue(propertyname: string[, default=None]): value |
Returns a value of the System Settings (Property) with the specified name ( Optionally, a The return value depends on the type of property. |
mycompany = vtcapp.getpropertyvalue("company") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
getseal(argobject.content) |
As of Vertec 6.8.0.16. The method checks whether the PDF document has been sealed. It is available to all customers, even without the Procurement & Purchases module. If the submitted PDF document does not have a seal,
|
vtcapp.getseal(argobject.content)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
getvertecserveraddress(): string |
Returns the address where the Vertec Cloud Server is available from the Internet. |
myurl = vtcapp.getvertecserveraddress()
Directly opens the Vertec App Portal in the browser: vtcapp.executeurl(vtcapp.getvertecserveraddress()) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
getwithsql(class: string, where: string, order: string, [idfilterfeld: string, objectlist: list]): list of objects
|
This global SQL statement is used to filter lists to be filtered directly on the database in a performance-optimized manner (see the article Performance-optimized access to vertec objects). A call via The executing user must have administrator rights or the SQL Query right. For granting temporary administrator rights, the variant of extended user rights is available.
In Vertec versions before 6.7.0.9 (before Firebird 5) lists (not the result list, but the filter criteria list, in the example on the right the |
Without optional filter criteria: projectlist = vtcapp.getwithsql("Project", "bold_id IN (SELECT project FROM phase WHERE status=1)", "code") With optional filter criteria: projects = argobject.evalocl("ownProjects") services = vtcapp.getwithsql("OpenService","", "entrydate", "project", projects)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
getwithsqlbymember(class: string, member: string, expression: string, order [optional]: string): list of objects |
Allows you to search objects of a class based on a single member string comparison for users without SQL privilege (the generic SQL search methods getwithsql and getmemberwithsql are subject to SQL user rights restrictions because they can be called with any SQL WHERE clause. The member must be of type string.
When the feature is called, the user rights of the current user are checked on the member used for the selection. The user must have class-wide read permission on the member for the search to work. Otherwise, an error occurs. |
projectlist = vtcapp.getwithsqlbymember("Project", "Code", "COM%") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
importconfigset(xmltext: string/file): stringBefore Vertec 6.7.0.7: importconfigset(xmltext: string/file) |
Import a config set into Vertec and apply it. As xmltext, valid XML text is passed as a string (UTF-8) or a config set. As of Vertec 6.7.0.7 the feature returns a string containing possible errors during the import. |
(name, file) = vtcapp.requestfilefromclient("Select Config Set", r"C:", "XML|*.xml") vtcapp.importconfigset(file) Or as an XML string: xml="""<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <configset name="test" author="test"> <requirements /> <references/> <objects/> <settings> <system-setting name="GlobalDokPfad">C:\Dokumente</system-setting> </settings></configset>""".encode('utf-8') vtcapp.importconfigset(xml) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
indexall([clean:boolean]) |
As of Vertec 6.8. Re-indexes all objects for Full Text Search. If clean is |
vtcapp.indexall()
keeps the current index and supplements it with the changed objects. vtcapp.indexall(True) discards the existing index and recreates it from scratch. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
indexclass(classname: string) |
As of Vertec 6.8. Re-indexes objects of the specified class for Full Text Search. If index configurations have been defined for the class passed with classname or if the System Settings for indexing documents or emails have been set for the class activity, all objects of this class are re-indexed with this feature. If these conditions are not met, then nothing is done. |
vtcapp.indexclass("Project") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
indexlist(objectlist) |
As of Vertec 6.8. The method takes a list of objects and re-indexes them for the Full Text Search. Objects for which no index should be written are automatically sorted out. It is also possible to pass a single object as a list. |
Indexing a single object:
vtcapp.indexlist([argobject])
Index list:
list = argobject.entries
vtcapp.indexlist(list)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
As of Vertec 6.8. This method can be used to re-index activities of a specific type for Full Text Search. One of the following values is passed as type:
|
vtcapp.indexactivities(1)
re-indexes all documents. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
indexstatus(): dict |
As of Vertec 6.8. Outputs indexing status information for Full Text Search-text search as a dictionary with the following information:
This information is also output to the System Info in the new Indexing area. Complex operations are |
print vtcapp.indexstatus() {u'OperationRunning': False, u'IsAvailable': True, u'StatusMessage': u'idle'} |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
indexabort() |
As of Vertec 6.8. Abort a current running indexing for Full Text Search. The queuing of the objects is canceled, already queued objects are indexed. |
vtcapp.indexabort()
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
indexstatistics(): IndexStatisticsResults |
As of Vertec 6.8.0.15. Returns the following information about the index of the Vertec full-text search als
|
vtcapp.indexstatistics()
Sample output:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
indexinfo(objid): IndexInfoResults |
As of Vertec 6.8.0.15. Returns information about the object passed via internal ID (objid) in the index as
|
vtcapp.indexinfo(12345)
Sample:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
inputbox(caption: string, prompt: string[, default: string]): string |
Show simple input field.
The structure of the buttons and the return values works according to article msgbox/inputbox: description of the parameters. |
vtcapp.inputbox("aTitle", "Insert a text:") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
log(category: string, level: int, msg: string) |
Log Message in Vertec Logging System. Possible levels:
For more information, see Logging. |
project = argobject service = project.evalocl("openServices->first") if service: try: service.xfeext = 0 except: vtcapp.log("Change Service", 30, "Access denied on xfeeext") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
msgbox(text: string [, buttons: int, title: string]): int |
Displays a message box. The feature supports (optional) arguments for buttons and titles. Buttons and return values work according to article msgbox/inputbox: description of parameters. |
vtcapp.msgbox("This is my message", 1, "Vertec") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
msgtomime(msgcontent): mimecontent |
From version 6.5.0.11. Convert
Existing emails as Note: With the Vertec Outlook App are stored directly on activities in MIME format. |
(name, file) = vtcapp.requestfilefromclient("Select email", r"C:", "Email|*.msg") mimecontent = vtcapp.msgtomime(file) activity = vtcapp.createobject("Activity") activity.setemailcontent(mimecontent) vtcapp.showdetailform(activity) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
pdfcombine(doc1:string, doc2:string): string |
This method merges 2 PDF documents. The PDF documents are passed as a byte string. |
newpdf = vtcapp.pdfcombine(pdf1, pdf2)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
pdfextract(doc:string, pagefrom:int, pagetill:int): string |
This method extracts one or more pages. The pagefrom and pagetill parameters correspond to the first and last page, respectively, and must be specified. |
newpdf = vtcapp.pdfextract(pdf1, pagefrom, pagetill)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
pdfpagecount(doc:string): int |
This method specifies the number of pages in the document. |
pages = vtcapp.pdfpagecount(pdf1)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
processbi(from: String, to: String, generator: String) |
Method for calculating Bi data for the Business Intelligence module. Corresponds to the calculation of the BI data on a Measure and triggers the calculation of the generator given as parameter. From and to dates are specified as a string in the format “Year-Month”. The generator must be specified in the same way as for the measures, i.e. “<Modulname>.<Generatorname>,” see example. Requires administrator rights. This method can also be automated, for example, via a scheduled task. To calculate all generators of all active metrics, see the method vtcapp.standardprocessbi() below. |
Example: From January 2024 to June 2025: vtcapp.processbi("2024-01", "2025-06", "ServicesGenerator.ServicesGenerator") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
querycallback(state): dict |
Retrieves a callback previously registered via registercallback(). As soon as the callback has been performed, the feature returns a dictionary with all supplied parameters (including state). As long as the callback has not yet been performed, the function returns a dictionary with all supplied parameters (including state). Callbacks that have already been successfully queried cannot be queried again, because the registration is then no longer available. When querying via querycallback() in a loop (polling), it is important to have a delay with the help of |
state=vtcapp.registercallback() # Example only. Call via OAuth authentication instead. vtcapp.executeurl("https://myserver.vertec-mobile.com/callback?State={}&message=ASecretMessage".format(state)) # Wait until browser is open. time.sleep(3.0) values=vtcapp.querycallback(state) print(values["message"]) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
readinvoicedocument(bytestream): resultobj |
The readinvoicedocument() feature accepts vendor documents in the formats Returns a Python object with the following attributes:
*Optional data: will only be output if the QR code contains additional information. |
name, receipt = vtcapp.requestfilefromclient("Select receipt", r"C:\Documents", "*.pdf;*.jpg;*.png") resultobj = vtcapp.readinvoicedocument(receipt) suppliers = vtcapp.getwithsqlbymember("Address", "name", resultobj.Name) supplier = suppliers[0] currency = vtcapp.getwithsqlbymember("Currency", "designation", resultobj.Currency)[0] creditor=vtcapp.createobject("Creditor") creditor.supplier = supplier if not creditor.documentdata: creditor.documentdata = vtcapp.createobject("DocumentData") creditor.documentdata.data = receipt creditor.accountnumber = resultobj.Account creditor.reference = resultobj.Reference creditor.currency = currency creditor.amountgross = resultobj.Amount if hasattr(resultobj, 'DocumentNumber'): creditor.number = resultobj.DocumentNumber if hasattr(resultobj, 'DocumentDate'): creditor.entrydate = resultobj.DocumentDate if hasattr(resultobj, 'DueDate'): creditor.xduedate = resultobj.DueDate if len(creditor.outlays) == 1: outlay = creditor.outlays[0] outlay.quantity = None outlay.xfeeintfcgross = resultobj['Amount'] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
registercallback(): string |
Registers a callback on the Cloud Server to transmit an authentication code. This is required, for example, for Authentication via oauth. The return value is a randomly generated state string, which must be passed in the callback in order to be accepted. The callback is executed as an http get request to the Cloud Server, as an example The parameters transmitted with the callback can then be queried via querycallback(). |
state=vtcapp.registercallback() # Example only. Call via OAuth authentication instead. vtcapp.executeurl("https://myserver.vertec-mobile.com/callback?State={}&message=ASecretMessage".format(state)) # Wait until browser is open. time.sleep(3.0) values=vtcapp.querycallback(state) print(values["message"]) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
rendertemplate(templateString, data): unicode string |
General-purpose template engine in Python, based on the Jinja2 template engine (http://jinja.pocoo.org). It is also available restrict scripting Cloud Suite and returns a Unicode string.
The main structures are as follows:
|
# Example code for the output of a project list templateText = """ My own projects =============== {% for proj in projects %} Project: {{ proj.code }}, {{ proj.description }} {% endfor %} =============== """ projects = vtcapp.evalocl("Session->first.login.ownProjects") rendered_text = vtcapp.rendertemplate(templateText, projects = projects) print rendered_text |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
renewdatabaseindexstatistics() |
As of version 6.8. Recalculate the index statistics, see the article Database performance and index statistics. |
vtcapp.renewdatabaseindexstatistics()
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
requestfilefromclient(dialogTitle: string, directory: string, filter: string [, fileName: string]): (filename, file)The format can contain several file types per filter. |
The user can select a local file in the client application, which is then transferred to the server and is available as a binary stream for further processing by the Python method.
The method returns a tuple consisting of file names and file contents (before version 6.4.0.22 the method returns a tuple consisting of absolute file path including file names and file contents). The maximum size of the file to be uploaded is 50 MB. If the user clicks on Cancel in the dialog, the error message appears in Python: Web App If a client-side path is specified (parameter The start directory (parameters In versions prior to 6.4.0.8 the file dialog cannot show a custom dialog title. The parameter For the filter, the designation is not shown, it only says “All support types (...)” and then the suffixes individually. |
vtcapp.requestfilefromclient("Select file", r"C:\Documents", "Python|*.py|Text|*.txt|XML|*.xml")
A simple syntax is also supported: vtcapp.requestfilefromclient("Select file", r"C:\Documents", "*.txt") Or a direct upload: vtcapp.requestfilefromclient("", "", "", r"C:\Documents\MyFile.txt") If a directory cannot be accessed, an error message is thrown: vtcapp.requestfilefromclient("Select file", r"C:\Windows\System32", "*.dll") Version before Vertec 6.3.0.12: vtcapp.requestfilefromclient("Select file", r"C:\Documents", "Python|.py,Text|.txt,XML|.xml")
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
roundcurrency(amount, currency=None): float |
Rounds the specified amount, taking into account the Project > Use rounding rules Use commercial rounding rules setting. If a Currency is optionally entered, the value |
Without currency indication:
amount = argobject.total
vtcapp.roundcurrency(amount)
5105.89
With currency indication:
amount = argobject.total
curr = argobject.currency
vtcapp.roundcurrency(amount, curr)
5105.9
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
search(term:string, [language:string, withsuggestions:boolean, datetimefrom: date, datetimeto:date, onlyactive:boolean, classfilter:stringlist]): SearchResultPerforms a Full Text Search in the indexed objects.
The method uses keyword arguments, so the optional parameters can be passed as follows:
Returns a Python object of type SearchResult. It contains the following properties:
A search returns a maximum of 500 business objects (SearchResultItems). These are sorted in descending order of relevance (score). |
results = vtcapp.search("keller", "EN", False, datetimeto=vtcapp.currentdate()) for item in results.items: print item, item.fragments With results = vtcapp.search("consulting") projects = results.objects.evalocl("self->select(oclIsTypeOf(Project))") Or, as of Vertec 6.8.0.15, with classfilter: results = vtcapp.search("keller", "DE", False, datetimeto=vtcapp.currentdate(), classfilter=["Project"]) projects = results.objects
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
sealpdf |
As of Vertec 6.8.0.16. The PDF document passed as a If a |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
scriptexecute(scripttext, argobject=None) |
Allows calling a Vertec script.
|
proj = vtcapp.getobjectbyentryid("Project", "TemplateProject") scripttext = vtcapp.evalocl("script->select(designation='Copy project')->first.scripttext") vtcapp.scriptexecute(scripttext, proj) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
selectaddress()selectphase()selectproject()selectobjectintree() |
From version 6.4.0.21. Allow calling the different search and selection dialogs for addresses, projects, phases and the tree directly from Python. The methods support the following optional keyword arguments:
Return value is the selected object. |
adresse= vtcapp.selectaddress(title="Address selection", classname="Contact", filter="firstname like '%S%'") projekt = vtcapp.selectproject(title="Project selection", filter="code like '%S%'") phase= vtcapp.selectphase(title="Phase selection", filter="code like '%S%'") contacts= argobject.subfolders contactfolders = list(contacts) contactfolders.append(argobject) selected=vtcapp.selectobjectintree("Select object", contactfolders, "Folder, Contact", selectfilter="Contact") |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
selectfromlist (caption: string, text: string, col1caption: string, col2caption: string, default: string, list: list of tuple): string |
Creates a selection dialog according to the specifications.
The feature returns a string with the selected value. Only one value can be selected from the list. *) To pre-select a row, the tuples of the list rows must consist of 3 elements. The third element is then the return value when the row is selected (this third column is invisible): vtcapp.selectfromlist("","","","","2",[("one","eins","1"),("two","zwei","2")])Only in this case does the default parameter have an effect: it then preselects the row whose third column corresponds to the specified default. |
projectlist = [] projects = vtcapp.evalocl("Session->first.login.ownProjects") for project in projects: projectlist.append((project.code, project.regarding)) vtcapp.selectfromlist("Project selection", "Select a project:", "Code", "Regarding", "", projectlist) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
sendfile(file: string, filename: string, [showsavedialog: boolean], [openfile: boolean]): booleanSends a file or string (as a file) to a client. Also works in Restricted Scripting mode.
As of Vertec 6.5.0.11 the suppression of a dialog is only possible for the following file types (extensions). Whitelist:
The combination The method has a return value and returns True or False:
Example of a simple project export: projects = argobject.evalocl("ownprojects.list") projectstr = "" for project in projects: projectstr += project.code + "\r\n" vtcapp.sendfile(projektstr, 'projects.txt', True, True) Example of how to send a locally available image: filename = r"C:\Projects\python_editor.png" # opening for [r]eading as [b]inary with open(filename, 'rb') as afile: vtcapp.sendfile(afile, 'aFilenameHere.jpg', True, True) Files should be explicitly closed after use. Otherwise, they will only be closed by the garbage collector or, in case of failure, on the next exception. It is recommended to use |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
sendmail(to, subject, body, [cc, bcc, fromSender, attachments])Allows sending emails from Vertec with the requirements described in System Settings Email. This method can be used with all apps.
Optional:
Examples:
vtcapp.sendmail("myemail@company.com", "Documentation", "This is the simplest case")
1. The corresponding Word document must be created and read: in_file = open("C:\<yourPath>\ExcampleWordForEmail.docx", "rb") dataFileData = in_file.read() 2. Use the method to generate the email: vtcapp.sendmail('myemail@company.com', 'Test email from Word', dataFileData) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
setpropertyvalue(name, value) |
Sets a system setting. The corresponding name is specified for each system setting. |
vtcapp.setpropertyvalue('BlockingDate', vtcapp.incmonth(vtcapp.currentdate(), -1)) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
setresourceplanvalue
|
Only Vertec versions before 6.6. From Vertec version 6.6 onward, use the Sets a resource plan value.
|
user= vtcapp.currentlogin() project= argobject vtcapp.setresourceplanvalue(user, project, None, vtcapp.firstdayofmonth(vtcapp.currentdate()), 0, 240) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
showcustomdialog(dialog definition, initial values) |
Dialog function with which dialogs can be defined in Python scripts and shown by the script. |
A detailed description can be found in the article about the Python dialogs. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
showdetailform(obj: object) |
Displays the detail view of the object in a new tab. |
service = vtcapp.createobject("OpenService") vtcapp.showdetailform(service) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
standardprocessbi() |
Method for calculating Bi data for the Business Intelligence module. Corresponds to the execution of the planned task supplied by default and triggers the calculation of all generators on all active measures. Requires administrator rights. To calculate individual generators, see the method vtcapp.processbi() above. |
vtcapp.standardprocessbi()
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
strtominutes(string): integer |
Translates a string to a minute value (integer), taking into account the current set system setting setting. |
Display minutes is hours:minutes: print vtcapp.strtominutes('1:30') >>> 90 print vtcapp.strtominutes('1.50') >>> 110 Display minutes is hours.Decimal: print vtcapp.strtominutes('1.50') >>> 90 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
sqldateliteral(date: date): string |
This method returns the correct date format for SQL queries, depending on the database server used, which is then converted into a getwithsql statement can be built in. |
activities = vtcapp.getwithsql('Activity', 'entrydate = %s' % vtcapp.sqldateliteral(vtcapp.currentdate()), '') for act in activities: print act |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
sqlwhere(where: string): string |
Creates a SQL WHERE clause matching the current database server, which can then be placed in a The fuction does the following:
|
whereclause = vtcapp.sqlwhere("standardstreetaddress like 'Main%'") addresses = vtcapp.getwithsql("Address", whereclause, "bold_id") print whereclause >>> upper(standardstreetaddress) starting with 'MAIN' |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
query:string, from: date, to: date): string |
Creates a SQL between clause with a date interval corresponding to the database server current in use, which is then |
today = vtcapp.currentdate() whereclause = vtcapp.sqlwherebetweendate('entrydate', vtcapp.firstdayofmonth(today), today) print whereclause >>> entrydate between '01.08.2025' and '07.08.2025' |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
syncpayments() |
Starting with version 6.4.0.22. Performs a global payment import. If no debtor extension with payment import is installed, the function reports an error. |
vtcapp.syncpayments()
The function can also be registered as a Scheduled task if the installed debtor extension is an online extension(cloud capability: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
SystemContext() |
As of version 6.6. Activates Extended user rights within the script.
|
with vtcapp.SystemContext(): ...code running in system context |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
translate(txt: string[, language:string]): string |
Translates a text into the current Vertec language. An optional parameter for the target language of the translation can be used. See also article Multilingualism with vertec. |
The current Vertec language is English: >>> vtcapp.translate("Leistung") Service Specifying the target language: >>> vtcapp.translate('Service', 'FR') Prestation |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
updatedatabase() |
Saves changes to the database. |
vtcapp.updatedatabase()
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
validateobjects() |
Validates rebuild objects. If they do not violate any rules, they are no longer invalid afterwards. |
vtcapp.validateobjects()
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
versiontointeger(versionstring): int |
Converts a Vertec version string to a number suitable for comparing different versions. |
>>> vtcapp.versiontointeger("6.8.0.7") 6800007 >>> vtcapp.versiontointeger("6.8") 680000 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Date Functions
The following date functions are available. They are all located in the vtcapp module.
| Function | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
currentdate(): date |
Returns the current date. |
>>> vtcapp.currentdate()
2025-01-23
|
currentdatetime(): datetime |
Returns the current date and time. |
>>> vtcapp.currentdatetime()
2025-01-23 15:01:12.880000
|
datetostr(date): string |
Converts a date to a string and returns it according to the country settings. |
For example, English (UK): >>> vtcapp.datetostr(argobject.evalocl("entrydate")) 14/06/2025 |
datetostrgerman(date): string |
Converts a date to a string and returns it in German date format. It sometimes needs German date values in some locations in scripts, regardless of current region settings (see e.g. from/to arguments in groupperformance operators). |
>>> vtcapp.datetostrgerman(argobject.evalocl("entrydate")) 14.06.2025 |
firstdayofmonth(date): date |
Returns the date of the first day of the same month |
>>> vtcapp.firstdayofmonth(vtcapp.currentdate()) 2025-08-01 |
firstdayofyear(date): date |
Returns the date of the first day of the same year |
>>> vtcapp.firstdayofyear(vtcapp.currentdate()) 2025-01-01 |
formatminutes(integer): string |
Returns hour-minute display according to System Settings in Vertec |
>>> vtcapp.formatminutes(argobject.minutesext)
1:20
|
incday(date, integer): date |
Increments the day (+ or -) and returns the new date |
>>> vtcapp.currentdate() 2025-08-08 >>> vtcapp.incday(vtcapp.currentdate(), 1) 2025-08-09 >>> vtcapp.incday(vtcapp.currentdate(), -1) 2025-08-07 |
incminute(datetime, integer): datetime |
Increments minutes (+ or -) and returns a new date. The date that is passed must be in datetime format, i.e. have a time fraction. |
Adds 4 hours to the current time:
>>> vtcapp.incminute(vtcapp.currentdatetime(), 240) 2025-08-08 16:27:48.432000 |
incmonth(date, integer): date |
Increments month (+ or -) and returns the new date Note: If the date is at the end of the month and the respective months have a different quantity of days, the last day of the month is used. Example: |
>>> vtcapp.incmonth(vtcapp.currentdate(), -1) 2025-07-08 |
incyear(date, integer): date |
Increments the year (+ or -) and returns the new date |
>>> vtcapp.incyear(vtcapp.currentdate(), -1) 2024-08-08 |
lastdayofmonth(date): date |
Returns the date of the last day of the same month |
>>> vtcapp.lastdayofmonth(vtcapp.currentdate()) 2018-03-31 |
lastdayofyear(date): date |
Returns the date of the last day in the same year |
>>> vtcapp.lastdayofyear(vtcapp.currentdate()) 2025-12-31 |
ocldate(date): string |
Returns OCL encodedate string based on a date value |
>>> vtcapp.ocldate(vtcapp.currentdate()) encodedate(2025,8,8) |
strtodate(string): date |
Interprets a date string according to Windows locale settings (see notes on using strtodate below). |
>>> vtcapp.strtodate('15.8.25') 2025-08-15 |
thismonday(date): date |
Returns the date of Monday in the same week |
>>> vtcapp.thismonday(vtcapp.currentdate()) 2025-08-04 |
Note on the use of strtodate
The use of strtodate is tricky because the string is interpreted according to Windows locale settings. So the expression returns vtcapp.strtodate('31.01.2024') an error if it is not German country settings.
Therefore, the Python date function should always be used in the code datetime.date(year, month, day) can be used.
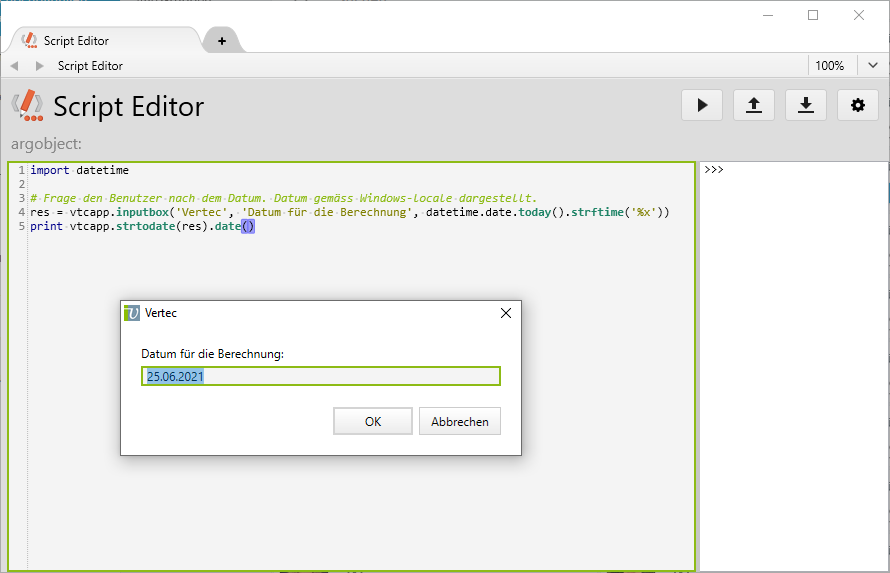
However, if, for example, the user wants to query a specific date via an input box, you can do this by presenting him with a suggested date in the correct format, which he can modify accordingly.
For this, the date is formatted according to local country settings (vtcapp.datetostr..):
# Frage den Benutzer nach dem Datum. Das Datum wird gemäss Windows-locale dargestellt. res = vtcapp.inputbox('Vertec', 'Datum für die Berechnung', vtcapp.datetostr(vtcapp.currentdate()))
Availability of executereport() with different systems
italics: optional parameter
| executereport(rootObj, optarg, reportObj, [saveAs, showDialog, doPrint, showApp]) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reporting system | ReportObj | saveAs | showDialog | doPrint | showApp | Desktop | Cloud | Web |
| Office-generated legacy reports (Word, Excel) | Report object in Vertec
or Path to the Office template on the file system. |
If an empty string is specified or the argument is omitted, no file is saved. |
True or False
Default=False |
True or False
Default=False No longer considered in versions 6.6.0.8 or later. |
True or False
In versions before 6.6.0.8 disregarded if doPrint = True. In this case, the report is always shown. disregarded if report is not saved. In this case, the report is always shown. |
x | x | |
| Vertec-generated legacy word reports | Report object in Vertec | Dito | Dito | Not included | Not included | x | x | x |
| Office reports (Word, Excel, PDF) | Report object in Vertec | Dito | Dito | Not included | True or False
Disregarded if report is not saved. In this case, the report is always shown. |
x | x | x |
| executereport2(rootObj, optarg, reportObj, [saveAs, showDialog, doPrint, showApp]) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reporting system | ReportObj | saveAs | showDialog | doPrint | showApp | Desktop | Cloud | Web |
| Office-generated legacy reports (Word, Excel) |
Report object in Vertec No paths. |
If an empty string is specified or the argument is omitted, no file is saved. If no file is saved, no activity is created. |
True or False
Default=False |
True or False
Default=False No longer considered in versions 6.6.0.8 or later. |
True or False
In versions before 6.6.0.8 disregarded if doPrint = True. In this case, the report is always shown. disregarded if report is not saved. In this case, the report is always shown. |
x | x | |
| Vertec-generated legacy word reports | Report object in Vertec | Dito | Dito | Not included | Not included | x | x | x |
| Office reports (Word, Excel, PDF) | Report object in Vertec | Dito | Dito | Not included | True or False
Disregarded if report is not saved. In this case, the report is always shown. |
x | x | x |
Features on individual vertec objects
The following Python features are available on individual objects depending on the class (type).
The class of an object can be determined in Python using OCL:
obj.evalocl('ocltype.asstring')
All objects
On all objects, regardless of the class, there are the following Python features:
| Function | Description | Sample code |
|---|---|---|
addtag(tagname) |
Sets a tag on the object. For more information, see Tags on user records. |
argobject.addtag('mytag') |
checkright(right: string, membername: string): boolean |
Checks whether the logged-in user has the specified right on the specified member name. Possible rights are: 'read’, 'write’, 'create’, 'delete’, 'execute’ Return value: 1 = True, 0 = False |
obj = argobject if obj.checkright('read', 'openservice'): ... |
delete() |
Deletes the object in Vertec |
obj.delete()
|
evalocl(OCL:string) |
Evaluates an OCL expression on the object. |
code = argobject.evalocl("code") |
getattr(object, name[, default]) |
Returns the value of a member.
If there is no member of this name on the object, the method returns the default if one is specified. Otherwise, there is an AttributeError. With hasattr() you can query whether a member of this name exists. With setattr() you can write a member. |
getattr(obj, "firstname", "") project = argobject if hasattr(project, "openservices"): list = getattr(project, "openservices") for service in list: print service.text |
getkeystring(key): stringgetkeybool(key): booleangetkeycurr(key): currencygetkeyint(key): integergetkeydate(key): datetime |
These methods are used to access the values stored as key values. Details can be found in the article Key values on user entries. |
argobject.getkeycurr('dailytotal') |
getmemfootprint(): integer |
Returns the quantity of bytes that the object occupies in memory (memory footprint). The value is determined as follows: Instance of the object + Sum of instances of all members + Size of the value of each member (for strings the length) + MemFootPrint of all owned linked objects (e.g. phases of the project). It should be noted that this is an approximation, since the boundary of what must be counted for an object cannot be drawn exactly. |
projects = argobject.evalocl("ownprojects") for project in projects: print "{} {}".format(project.code, project.getmemfootprint()) |
getmlvalue(membername:string, language:string): value |
The so-called multilanguage attributes (MLStrings) can be queried via this method.
Multilanguage attributes are:
To set such an attribute, the method setmlvalue() can be used. In the case of a normal query, e.g. |
servicetype = argobject.evalocl("type") if servicetype: print servicetype.getmlvalue("text", "FR") Important to note: If no value is entered on the Mlstring for the respective language code – for example, because the NV (native) term is Vertec Translation System translated by the Vertec translation system, this query does not query show the translated value, but an empty string. |
hasattr(object, name): boolean |
Checks whether an object has a corresponding member. Useful e.g. on a list of addresses where it is not known whether the individual object is a person or a company, etc. Also used before calling the gettattr() or the setattr() function. |
if hasattr(obj, "firstname"): obj.firstname |
hastag(tagname): boolean |
Checks whether an object has set a corresponding tag. For more information, see the article Tags on user entries. |
if obj.hastag('mytag'): ... |
istypeof(Classname:string)or IsTypeOf(Classname:string): boolean |
Checks whether the object is of type Classname. |
if obj.IsTypeOf("Project"): ... |
linkto(target, Role) |
Makes a link type from the object to the passed object (target) with the specified Role. For detailed information on this topic, see the article Operators and methods for links. |
person = argobject account = vtcapp.getobjectbyid(2995) account.linkto(person, "BoD") |
objid |
Returns the internal ID of the object. |
>>> argobject.objid 3011 |
removetag(tagname) |
Deletes the corresponding tag from this object. For more information, see the article Tags on user entries. |
argobject.removetag('mytag') |
setattr(object, name, value) |
Describes the name attribute of the object object with the value value. For example, you can loop through the custom field items of an object and use the found attribute names to describe the attributes. |
This code creates a new object of the same type as the argobject and copies the contents of all additional fields to the new object. source = argobject target = vtcapp.createobject(source.evalocl('ocltype.asstring')) items = source.customfielditems for item in items: iName = item.customfield.fieldname Now you know the name of the additional field, but if you address it with setattr(target, iName, getattr(source, iName)) |
setkeyvalue(key, value) |
With this method, customer-specific values are stored as key values on user entries. These values can be accessed later via the |
projects = argobject.evalocl("ownprojects") dailytotal = projects.evalocl("openservices.feeext->sum") argobject.setkeyvalue("dailytotal", dailytotal) |
setmemberoutofdate(membername:string) |
If a value is to be read freshly from database, the field out of date must be set. This method does the same as the Notif for a Modified message. |
proj = argobject proj.setmemberoutofdate('code') ensures that the next time you access Projekt.code, this value is loaded freshly from the database. |
setmlvalue(membername:string, value:string, language:string) |
The so-called multilanguage attributes (MLStrings, multilingual attributes) can be set via this method.
To retrieve such an attribute, the method getmlvalue() can be used. |
servicetype = argobject servicetype.setmlvalue("text", "Vacanze", "IT") |
unlink(target, Role) |
Removes the link from the object to the passed object (target) with the specified link role. For detailed information on this topic, see the article Operators and methods for links. |
person = argobject account = vtcapp.getobjectbyid(2995) account.unlink(person, "BoD") |
unload() |
Removes the object from the Vertec object store. This method was introduced solely to control memory usage during data migrations. It should be used with caution, as subsequent accesses to the unloaded object can result in errors. |
|
Projects
On individual objects of the class Projekt there are the following Python features:
| feature | description | Sample code |
|---|---|---|
entrytypeslookup(typidx, phase=None, user=None): List of projectcostitemtypes |
Returns a list of cost item types for the project to which entries can be entered. One of the following values is passed as typeidx:
Optionally, a phase and from Vertec 6.8.0.9 onwards also a user can be passed. Then only project entry types are returned, which also fit the phase and/or the user (see Phase Specifications). |
proj = argobject user = vtcapp.currentlogin() phase = vtcapp.getobjectbyid(24509) servicetypelist = proj.entrytypeslookup(0, phase, user) |
phaseslookup(user, entrytype=None): List of phases |
Returns a list of phases (and optionally a cost item type) for the specified user to which they can enter. |
proj = argobject user = vtcapp.currentlogin() servicetype = vtcapp.getobjectbyid(1969) phaselist = proj.phaseslookup(user, servicetype) oder phaselist = proj.phaseslookup(user, None) |
projektbearbeiterisassigned(user): boolean |
Specifies whether the specified user is authorized to create services etc. on this project. |
proj = argobject user = vtcapp.currentlogin() if proj.projektbearbeiterisassigned(user): ... |
|
setresourceplanvalue(worker, date, value) |
As of Vertec 6.6. Allow the setting of resource plan values when the is set to project.
|
user = vtcapp.currentlogin() project = argobject project.setresourceplanvalue(user, vtcapp.strtodate('15.05.2025'), 180) |
AbstractWorker
AbstractWorker is the base class of Users and Planning Editors. On individual objects of these classes there are the following Python features:
| feature | description | Sample code |
|---|---|---|
setresourceplanvalue(project_or_phase, date, value) |
Vertec 6.6 and later. Allows the setting of resource plan values.
|
bearb = vtcapp.currentlogin() projekt = argobject bearb.setresourceplanvalue(projekt, vtcapp.strtodate('15.05.2023'), 180) |
User
On individual objects of the class User there are the following Python features:
| Function | Description | Sample code | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
isBlockedDate(date [, subscriber=None]): Boolean |
As of Vertec 6.8.0.12. Returns
|
date1 = vtcapp.currentdate() # argobject is a user argobject.isblockeddate(date1) |
||
setnotification(category, text, link) |
As of Vertec 6.6. Add a Notification (Notification) to the user with specified category, text and optionally linked User Entry. If a notification with the same category and the same linked object already exists on the user, the text is updated.
|
aktivitaet = argobject zustaendig = aktivitaet.zustaendig if zustaendig and not aktivitaet.erledigt: zustaendig.setnotification('pending_activity', aktivitaet.titel, aktivitaet) |
||
deletenotification(category, link) |
As of Vertec 6.6. Delete the Notification (Notification) on the user with the corresponding category and linked object. If no corresponding notification is found, nothing happens. No error message appears. |
aktivitaet = argobject zustaendig = aktivitaet.zustaendig if zustaendig and aktivitaet.erledigt: zustaendig.deletenotification('pending_activity', aktivitaet) |
Phases
On individual objects of the class Projektphase there are the following Python features:
| feature | description | Sample code |
|---|---|---|
setresourceplanvalue(worker, date, value) |
As of Vertec 6.6. Allow the setting of resource plan values when the Planning Level is set to phase.
|
bearb = vtcapp.currentlogin() phase = argobject phase.setresourceplanvalue(bearb, vtcapp.strtodate('15.05.2023'), 180) |
Invoices
On individual objects of the class Rechnung there are the following Python features:
| feature | description | Sample code |
|---|---|---|
book([raiseException]) |
Posts an invoice to accounting. The raiseException argument is a Boolean (True/False) that indicates whether errors should be reported when posting or cancelling. raiseException is optional, default is True. If raiseException is False, then errors during posting are ignored, the invoice is simply not posted. |
rechnung = argobject rechnung.buchen() |
import payments() |
Imports the payments to the current invoice. Work only if the customer interface supports payment import. |
argobject.importzahlungen() |
makeoffen([raiseException]) |
Sets a settled invoice back to open (charging). The raiseException argument is a Boolean (True/False) that specifies whether errors should be reported during charging or undone during charging. raiseException is optional, default is True. If raiseException is False, then errors are reversed and the invoice simply remains charged. |
rechnung = argobject rechnung.makeoffen(False) |
makeverrechnet([raiseException]) |
Charges an open invoice. The raiseException argument is a Boolean (True/False) that specifies whether errors should be reported during charging or undone during charging. raiseException is optional, default is True. If raiseException is False, then errors will be ignored, leaving the invoice open. |
rechnung = argobject rechnung.makeverrechnet(False) |
cancel([raiseException]) |
Cancels a posted invoice. The raiseException argument is a Boolean (True/False) that indicates whether errors should be reported when posting or cancelling. raiseException is optional, default is True. If raiseException is False, then errors in the post are ignored, the invoice is simply not cancelled. |
rechnung = argobject rechnung.stornieren() |
Project Entries
With the class Projekteintragservices, expenses and outlays are summarized. On individual objects of these classes there are the following Python features:
| feature | description | Example code |
|---|---|---|
makeoffen() |
Sets a billed service, expense or outlay to open. This only works if the service, expense or outlay is not on an invoice, otherwise an error will be thrown. |
argobject.makeoffen() |
makecompute() |
Sets an open service, expense or outlay to charged. This only works if the service, expense or outlay is not on an invoice, otherwise an error will be thrown. |
argobject.makeverrechnet() |
Services
On individual objects of the class Leistung(OpenPower, BilledPower) there is the following Python feature:
| feature | description | Sample code |
|---|---|---|
update set() |
Hourly rate is recalculated (from rate system). Requires user rights |
argobject.updatesatz() |
Activities
On individual objects of the class Aktivitaet there are the following Python features:
| Function | description | Sample code |
|---|---|---|
setpath(path: string) |
Sets the document path to the activity when Document Storage is set to |
argobject.setpfad('C:\\Dokumente\\text.txt')
|
setdocumentcontent(filename, documentcontent, modifieddate [optional]) |
As of Vertec 6.7.0.15. Add a document to the activity if the Document Storage is
The activity will do the following:
After successful execution, the Document page is shown. If a document is already saved on the activity, an error is output. Note: The method can also be used if the document storage is not on |
(name, file) = vtcapp.requestfilefromclient("Dokument auswählen", r"C:", "Word|*.docx")
activity = vtcapp.createobject("Aktivitaet")
activity.setdocumentcontent(name, file)
vtcapp.showdetailform(activity)
|
setemailcontent(mimecontent) |
As of Vertec 6.7.0.15. Add an email to the activity.
The activity will do the following:
Upon successful completion, the email page will be shown. If a document is already saved on the activity, an error is output. |
(name, file) = vtcapp.requestfilefromclient("Email auswählen", r"C:", "Email|*.eml") activity = vtcapp.createobject("Aktivitaet") activity.setemailcontent(file) vtcapp.showdetailform(activity) |
Currency
On individual objects of the class Waehrung there is the following Python feature:
| feature | description | Sample code |
|---|---|---|
getkursto(currency: object, date: date): currency |
Returns the exchange rate for the corresponding date. | chf.getkursto(eur, vtcapp.currentdate()) |
Vertec Lists
All Python methods that return lists of business objects directly return a Vertec list.
- evalocl()
- getwithsql()
- getmemberwithsql()
resulting lists are thus directly Vertec lists.
Example: liste = vtcapp.evalocl("projekt->select(code.sqllike('A%'))")
Methods on vertec lists
| Method/Feature | description | Example code |
|---|---|---|
append(object) |
A list can be populated using the append() method. Only individual objects can be passed, not entire lists with append(). |
mylist = vtcapp.createlist('Projekt')
mylist.append(argobject) |
evalocl(OCL:string) |
An OCL expression can be dropped from the Vertec list. |
projektIds = argobject.evalocl("eintraege").idstring()
leistungen = vtcapp.createlist("OffeneLeistung", vtcapp.getwithsql("OffeneLeistung", "projekt IN (%s)" % projektIds, ""))
print leistungen.evalocl("wertext->sum") |
extend(list: list) |
The extend() method can be used to append another list to a Vertec list. This checks whether the vertec list is a derived list (e.g. |
projektIds = argobject.evalocl("eintraege").idstring()
leistungen = vtcapp.createlist("OffeneLeistung", vtcapp.getwithsql("OffeneLeistung", "projekt IN (%s)" % projektIds, ""))
leistungen.extend(vtcapp.createlist("VerrechneteLeistung", vtcapp.getwithsql("VerrechneteLeistung", "projekt IN (%s)" % projektIds, "")))
print leistungen.evalocl("wertext->sum") |
idstring() |
a common requirement in Python scripts is to formulate a SQL query with To do this, the IDs of a list of objects must be converted to a comma-delimited string.
|
>>> vtcapp.evalocl('Projektbearbeiter->allinstances').idstring()
300,676,7613,682,688,694 |
index(object) |
Returns the index of the object in the list. If the object occurs more than once, the lowest index is returned. Introduced for compatibility with Python lists (see below). |
>>> liste = vtcapp.evalocl("projekt.code")
>>> print liste.index('COMINSTALL')
25 |
insert(index, object) |
Inserts an object into the list at index. Introduced for compatibility with Python lists (see below). |
>>> liste = [123, 'xyz', 'miau', 'abc'] >>> liste.insert(3, 2009) >>> print liste [123, 'xyz', 'miau', 2009, 'abc'] |
remove(object) |
Removes the specified object from the list |
projektIds = argobject.evalocl("eintraege").idstring()
leistungen = vtcapp.createlist("OffeneLeistung", vtcapp.getwithsql("OffeneLeistung", "projekt IN (%s)" % projektIds, ""))
fl = leistungen.evalocl("self->select(bearbeiter.asstring = 'Judith Feller')")
for leistung in fl:
leistungen.remove(leistung)
The example above serves to show the
projektIds = argobject.evalocl("eintraege").idstring()
leistungen = vtcapp.createlist("OffeneLeistung", vtcapp.getwithsql("OffeneLeistung", "projekt IN (%s)" % projektIds, ""))
leistungen = leistungen.evalocl("self->reject(bearbeiter.asstring = 'Judith Feller')") |
Differences vertec and python lists
Vertec and Python lists differ in the following ways:
The + operator is not applicable to vertec lists. Code of the type
projektIds = argobject.evalocl("eintraege").idstring()
leistungen = vtcapp.getwithsql("OffeneLeistung", "projekt IN (%s)" % projektIds, "") \
+ vtcapp.getwithsql("VerrechneteLeistung", "projekt IN (%s)" % projektIds, "")does not work. An error appears: Instead, use
leistungen = vtcapp.getwithsql("OffeneLeistung", "projekt IN (%s)" % projektIds, "")
leistungen.extend(vtcapp.getwithsql("VerrechneteLeistung", "projekt IN (%s)" % projektIds, "")) or
leistungen = vtcapp.getwithsql("OffeneLeistung", "projekt IN (%s)" % projektIds, "")
leistungen += vtcapp.getwithsql("VerrechneteLeistung", "projekt IN (%s)" % projektIds, "") |
Python lists can be created from Vertec lists by using |
It is important to note that Vertec lists are “live”. This means that actions related to the logic of the list calculation can change, as shown in the following examples: With for l in list(argobject.offeneleistungen): l.delete() The following is a list of open services:
leistungen = phase.evalocl("offeneleistungen")
for l in leistungen:
l.makeverrechnet()If they are charged sequentially, they are automatically removed from the list. The effect is the same as above: Only half of the services are charged. Convert to a Python list instead:
for l in list(phase.evalocl("offeneleistungen")):
l.makeverrechnet() |
'count’, 'pop’, 'reverse’ and 'sort’ are only available on Python lists. If you use these methods, you would have to rewrite them or make the Vertec list back into a Python list with |
