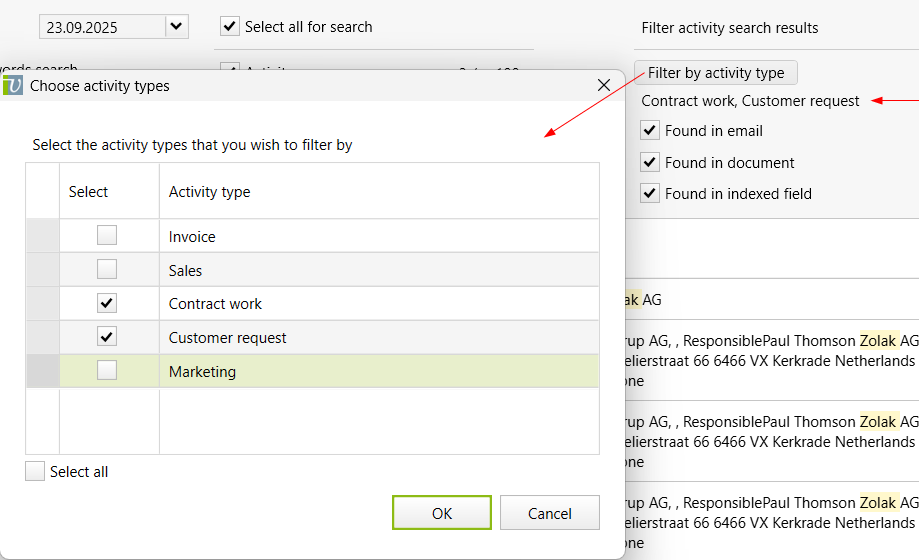
Vertec full-text search
How the full-text search works in Vertec
As of Vertec 6.8, Vertec features a full-text search function that searches emails (incl. attachments) and documents stored in Vertec in addition to the texts.
Clicking on the magnifying glass in the navigation menu (or F6 and F12) opens the Vertec search page:
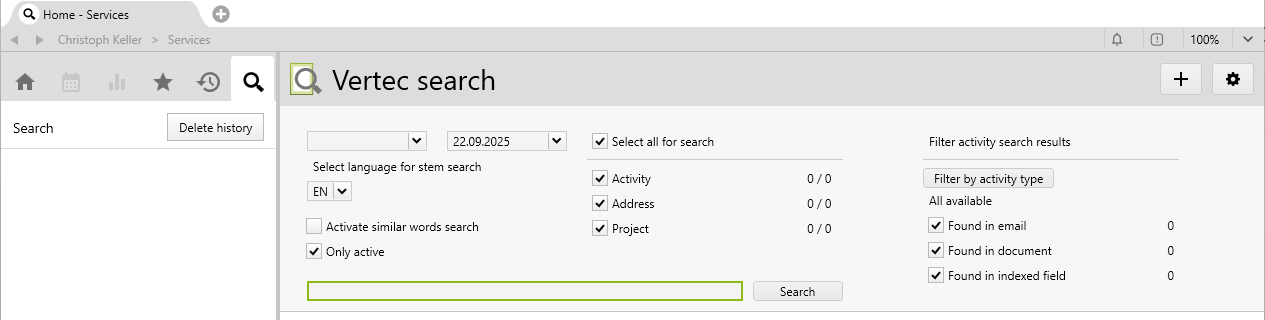
There are the following search fields:
Date from, to |
If you specify a date range, only search objects within that interval are considered. The date for the different search objects is the following:
By default, today's date is used as the To date. |
Select language for stem search |
The language selection for the word stem search is shown if additional languages for indexing are specified in the system settings. The word stem search means that, for example, a search for "house" will also find "houses". The word stem search is language-dependent. The search for "bikes" will only find "bike" if EN is selected as the language. By default, the language of the current user interface is pre-selected, if available. Otherwise the default language is used. |
Activate similar words search |
With this option, the search can be expanded to include similar terms if you feel that the exact search results are too few. This option is not used for umlauts, special characters, word stems, etc. These are already covered by the normal search, see section about the search syntax. For example, the normal search for "bear" also finds "bare" and "bears". With the similarity search turned on, "bank", "banks", "baron", etc., are also found. |
Only active |
If this option is activated (default), only active entries are shown in the result list.
|
Class selection |
As of Vertec 6.8.0.9, you can preselect the classes to be searched. All classes can be selected for which Index field definitions are available. If a class has specified a Display class name, this name is shown. With the checkbox |
Filter activity search results |
This area only appears if the class The search results of activities can be further filtered.
|
| Search term |
This term is searched for. How exactly this works is explained under the search syntax section. |
Click on Search or Enter to start the search. The results appear below:
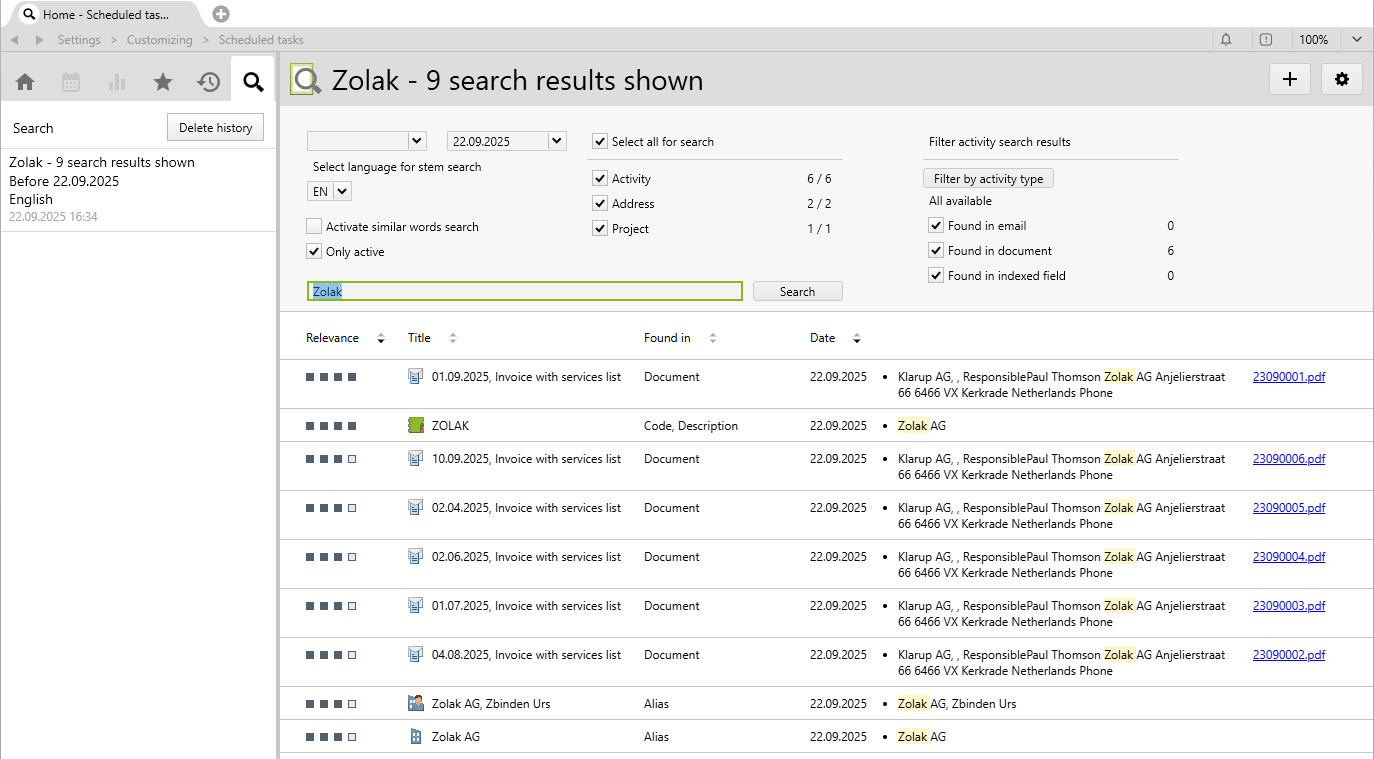
By default, the search results are sorted in descending order by relevance and date.
Double-clicking on a search result opens the relevant object.
Documents and email attachments in which the search term was found are shown as links and can be opened directly.
For activities, the project and the contact, if available, are also shown. These are also direct links to the relevant object:

A total of 500 search results will be shown, even if more than 500 entries were found in one search. Above, for each class, you can see how many entries are shown and how many were found in total (shown / found). This is especially useful if more entries have been found than can be shown:
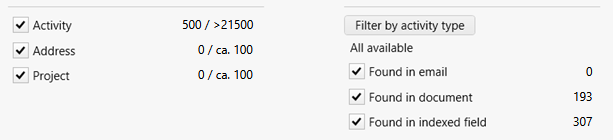
In this case, the search result can be narrowed down by adjusting the search and filter options.
The total of the objects found is given as follows:
- If all found objects can be shown,
shownandfoundare equal. - If objects of a class are shown, but in total more than 500 objects of this class are found, the total is shown in steps of 500, e.g.
>1500. - If no objects are shown by a class (because 500 objects from other classes are shown already), but some are found, then the total is rounded up in increments of 100, e.g.
ca. 100. - This is done because, for performance reasons, the read permissions are only determined when the result list is compiled. The approximate information does not allow precise conclusions to be drawn about the exact number.
The search syntax
Search for multiple terms
If more than one word is entered as a search term, the words are searched with AND, so only results containing a combination of the words are shown.
This can be adjusted as follows:
- Exact search with
quotation marks: Search terms can be enclosed in quotation marks. In this case, the entire term is searched. For example, the search for"Christoph Keller"only finds entries in which this term occurs. However, if you search forChristoph Keller, all the entries containing Christoph and Keller are found.- Note: A single word cannot be enclosed in quotation marks. Quotation marks are only effective with at least two words.
- Or search with
OR: The Or search can be used to search for several terms without having to find all terms in the same entry. The search forChristoph OR Keller
finds all entries in which either Christoph or Keller (or both) appear. - Exclude terms with
NOT: Certain terms can be excluded with NOT. The search forChristoph NOT Kellerfinds all the entries that contain Christoph, but not Keller. - The keywords
AND,NOTandORmust be written in capital letters.
Umlauts and special characters
Umlauts and special characters are ignored, in both indexing and in the search. For example, the search for “Müller” searches for “Muller” and thus finds both “Müller” and “Muller,”. The search for “Sørenson” finds “Sørenson,” “Sörenson” and “Sorenson”. This achieves the best results across all languages.
Stop words
A set of language-specific stop words that are not searched for, such as “and,” “in,” etc.
If a search term consists only of stop words, no results are shown.
Typographical errors
For typographical errors (typos), the Levenshtein distance is used If Activate similar words search is enabled. This means that a certain deviation is tolerated.
In the Vertec full-text search, the following rules apply:
- The search term must have at least three characters
- A mutation is allowed.
In English, the search for abcense (two characters swapped), absense (one character changed) or absnce (one character omitted), finds the term absence. In German, the search for Rechnugn (two characters swapped), Rechnunn (one character changed) or Rechung (one character omitted), finds the term Rechnung.
Word stem search
The word stem search means that, for example, the search for house also find houses.
The word stem search is always active automatically. It is language-dependent and is based on the language selected on the search page.
For example, the search for bikes, only finds bike if EN is the language selected.
In addition to the default language, the languages defined as additional search languages in the system settings are available for the word stem search.
Wildcard search
You can use the asterisk * as a wildcard to expand the search for the entered term. The asterisk replaces any number of characters.
Examples:
- The text of an activity contains the word
globalization. If you enter the wordglobal, the search does not find anything. However, if you enterglobal*it finds the relevant activity. - For indexed invoice numbers, searching for
0018will not find anything. However, if you search for*0018,you will find activities and invoices relating to the queried invoice number:

You can use the question mark ? to replace any character, allowing you to enter search terms with varying letters without having to enter each possible scenario individually.
Example:
- The search for
globali?ationfinds both the termsglobalizationandglobalisation.
Note: Using wildcards deactivates both the similarity search and the word stem search. This means, for example, that a search for globaal* or globaalisat?on delivers no results.
Configuring search fields
In the full-text search, all indexed data and documents are searched.
All objects for which at least one configuration is defined are considered. For this, there is a subfolder indexed fields in the
class settings on each class:

In addition, you can find an overview of all index field definitions in the folder Settings > Full-text search:

Here, you can define additional index fields and include them in the search index. The index configurations shown here are supplied by Vertec as the default.
Note: Indexing of documents and emails is not configured here. It is defined in the System settings for full-text search.
The index field definitions have the following attributes:
- Index type: Specifies the data source and is one of the following values:
- Field: The value is in a persistent database field. The index field must be a persistent member of the class.
- Key: The value is in a key on the data set. The index field must contain the name of the key.
- Custom fields: The value is in a custom field. The internal name of the custom field must be specified in the index field. This must be of type “Character," "ANSI Text" or "Text".
- Index label: String. Optional. The label shows the name with which the field value is written to the index. Therefore, it must be unique per object type (class).
The label is used later when the search results are displayed on the search page to indicate the field in which the search term was found. If no label is set, the value index field is shown instead.
- Index field: String. Specifies the field name, depending on the selected index type.
If new index fields are defined, the indexing must be refreshed before corresponding results appear. This can be done with one of the Python functions or with the scheduled tasks.